TRADING SYSTEM & INDEPENDENT GOVERNANCE
European Union Emission Trading System (EU ETS)
In 2005, the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) was launched, becoming the first and largest international carbon scheme in force.
The EU ETS covers approximately 40% of EU GHG emissions and includes more than 11,000 installations in the energy, domestic aviation and industrial sectors. It aims to reduce EU net GHG emissions by at least 55% by 2030 and reach climate neutrality by 2050.
The system works by setting a cap on emissions for each installation and allowing companies to trade allowances to emit a certain amount of GHGs. This has incentivized companies to reduce their emissions and invest in low-carbon technologies. Carbon credits from CDM and JI were allowed during several phases of the scheme.
International Carbon Reduction and Offset Alliance (ICROA)
The development and growth of carbon markets have also led to the establishment of international independent standards to ensure that carbon offsets contribute to the reduction of GHG emissions, while bringing transparency and credibility to the process.
In 2008, the International Carbon Reduction and Offset Alliance (ICROA), was established to set a framework for carbon offset projects in the Voluntary Carbon Markets.
ICROA is a non-profit membership organization, that promotes high-quality carbon credits with its Code of Best Practice, which its members sign up and report against.
There are currently 4 endorsed United Nations and government standards, and 9 independent standards.
INDEPENDENT CREDITING MECHANISMS
The term ‘voluntary carbon market’ (‘VCM’) historically referred to carbon markets operating outside the scope of a regulatory framework and governed by independent standards also referred to as ‘crediting mechanisms’ or ‘registries.
Standards play the role of market regulators, enabling the certification and issuance of carbon credits, and safeguarding the credibility of the market. Standards have become extremely complex with extended sets of rules, requirements, and methodologies. All credible VCM standards require independent 3rd party verification before carbon credits can be issued.
In recent years, the divide between voluntary and compliance markets has become less relevant as independent standards are increasingly being used in compliance markets and as governments engage in establishing domestic voluntary markets. Carbon markets are better defined by the nature of their supply, independent standards such as Verra (VCS) or Gold Standard (GS), versus government-led standards, and the nature of demand (i.e., voluntary demand vs compliance demand) that characterize them.
The most well-known independent standards are:
- American Carbon Registry (ACR) was founded in 1996 and was the first private voluntary GHG registry in the World.
- Climate Action Reserve (CAR) began as the California Climate Action Registry in 2001.
- Gold Standard was established in 2003 by the WWF and other international NGOs.
- Verra and the Verified Carbon Standard program was founded in 2005 by environmental and business leaders.
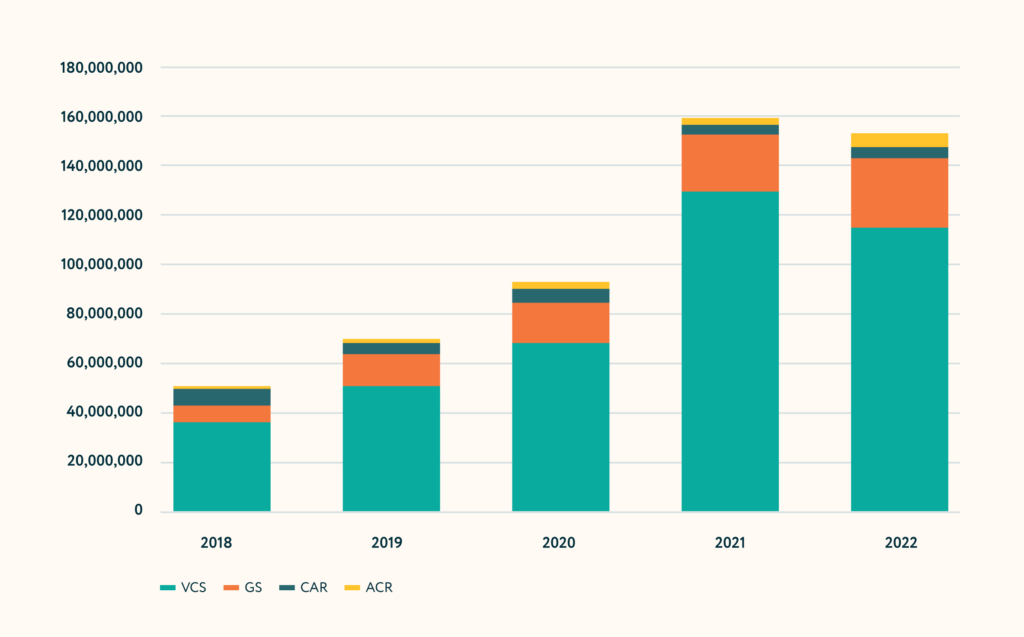
Figure 1.4. Total retired credits (tCO2) per standard 2018-2022 (including REDD+ projects).
Data extracted from SustainCERT Market Share Yearly Analysis 2022
In Lesson 2, we will go deeper into independent crediting mechanisms and other types of carbon pricing instruments.
