How are SDGs incorporated into the GS4GG Certification Process
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS (SDG)
The United Nations adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, in 2015. These goals serve as a universal call to action, aiming to eradicate poverty, safeguard the environment, and ensure peace and prosperity for all individuals by 2030. Comprising 17 interconnected objectives, the SDGs acknowledge that actions taken in one domain will have consequences in others, emphasizing the need for development that balances social, economic, and environmental sustainability.
Nations have pledged to prioritize advancements for those who are the most marginalized. The SDGs are specifically designed to address issues such as poverty, hunger, AIDS, and gender discrimination, with the ultimate goal of eliminating these challenges. Accomplishing the SDGs requires the collective involvement of society, drawing upon creativity, expertise, technology, and financial resources from all sectors in every context.

Read more about the Sustainable Development Goals (here).
PROJECT TYPES
To qualify as eligible for a project type, it must align with Activity Requirements and/or Approved Methodologies that are either published on the Gold Standard website or referenced in Gold Standard Product Requirements. In cases where a project type is not yet listed on the Gold Standard website, the Project Developer (PD) has the option to request approval for the project type during the Preliminary Review stage or earlier. It is important to note that the gold Standard does not endorse project types involving geoengineering, energy generation from fossil fuels or nuclear sources, fossil fuel switching, or any projects that promote, enhance, or prolong such energy generation. Gold Standard also does not provide support for such project type.
Community Services
- Renewable energy is connected to mini-grid or off-grid solutions.
- End-use energy efficiency
- Waste management + handling
- Water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH)
Renewable Energy Projects
- Projects must generate and deliver energy services using non-fossil fuel and renewable energy sources.
- Projects must use renewable energy generation units such as solar photovoltaic, tidal/wave, wind, hydro, geothermal, waste to energy, and renewable biomass that are either supplying energy to a national or regional grid or supplying energy to a specific consumer facility via the national/regional grid through a contractual agreement.
Afforestation/Reforestation (A/R) Projects
- A/R: Planting trees, single-species plantations, and various silvicultural systems, such as conservation forests, selective harvesting forests, and rotation forestry.
- AGR: Methane reduction by adjusted water management practice in rice cultivation.
- SOC: Increasing Soil Carbon through improved tillage practices, or application of improvers from paper and mill sludges.
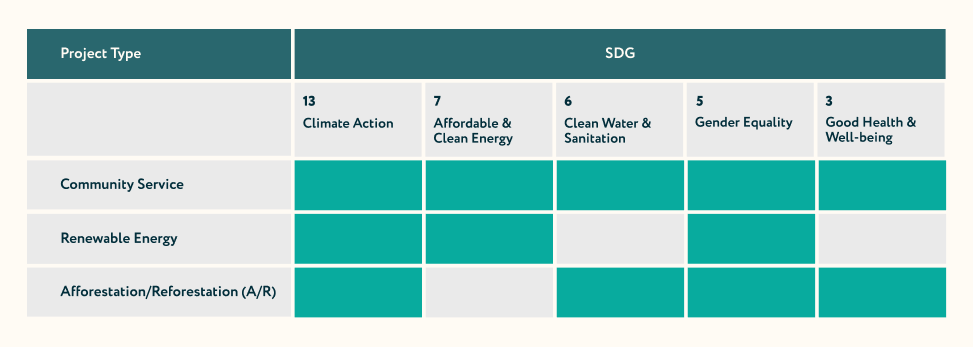
SDGS CLAIMED BY COMMON PROJECT TYPES
All GS4GG projects must demonstrate a positive contribution to SDG 13.
Emission reductions signify the avoidance of one metric tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO2e) from being released into the atmosphere. These reductions, commonly called carbon credits, are utilized for carbon offsetting purposes. The Gold Standard offers carbon credits in the following categories:
- Verified Emission Reductions (VERs) for voluntary climate action.
- Labels for Certified Emission Reductions (CERs).
What is eligible for claiming?
SDG 13: Climate Action
- By contributing to the Paris Climate Agreement and SDG 13, companies can enhance their credibility. To ensure credibility, it is recommended that companies initially commit to ambitious internal emission reduction targets, with the Gold Standard suggesting the establishment of Science-Based Targets. The purchase of emission reductions can then be utilized to fulfill claims of being ‘carbon neutral,’ ‘climate neutral,’ and even ‘climate positive.’
See GS Claims Guidelines, version 2.9 (09/06/2022)
All Renewable Energy projects are required to demonstrate a positive contribution to SDG 7.
The Gold Standard Renewable Energy Label certifies the generation and delivery of one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity from a renewable source to the electricity grid. This label guarantees that the buyer’s purchase leads to tangible emissions reductions in the real world and contributes to the expansion of renewable energy capacity in the grid. Moreover, the labeled energy comes from a project that has been verified to deliver sustainable development benefits.
At present, Gold Standard Renewable Energy Labels are issued in addition to International Renewable Energy Certificates (I-RECs) from the International REC Standard. Typical project types which claim this SDG are Energy Efficiency projects such as improved cook stoves, biogas, safe water access, etc.
What is eligible for claiming?
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy by 2030
- Target 7.1: Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix
- Target 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency
Contribution to SDG 6 represents a direct impact on ensuring the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation.
A Water Benefit Certificate signifies the sustainable supply, purification, or conservation of a specific volume of water. The volume assigned to each certificate varies based on the type of project, considering factors such as size and the extent of the provided impacts.
Typical project types which claim these SDGs are Safe Water Supply (SWS), such as boreholes, and water filters. etc.
What is eligible for claiming?
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.1. – Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all
- Target 6.2. – Achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all and end open defecation, paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations
- Target 6.3. – Improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing the release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally
- Target 6.4. – Substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity and substantially reduce the number of people suffering from water scarcity
- Target 6.5 – Implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including through transboundary cooperation as appropriate
All GS4GG Projects are “Gender Sensitive, signifying their adherence to the latest best practices in gender equality.
Promoting the empowerment of women and girls is recognized as a highly impactful approach to combatting climate change. By closing the gender gap, progress can be accelerated across numerous other Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The Gold Standard for the Global Goals prioritizes gender equality by implementing enhanced safeguards, ensuring that all Gold Standard projects are “Gender Sensitive.” Furthermore, projects could actively evaluate and certify their contributions to SDG 5 by adhering to the “Gender Responsive” Framework provided by the Gold Standard.
Typical project types which claim this SDG are biogas, improved cook stoves, access to clean water, etc.
What is eligible for claiming?
SDG 5: Gender Equality
- SDG Target 5.1: Ending all forms of discrimination against women and girls worldwide.
- SDG Target 5.4: Recognizing and valuing unpaid care and domestic work through the provision of public services, infrastructure, social protection policies, and promoting shared responsibility within households and families as appropriate on a national level.
- SDG Target 5.5: Ensuring women’s full and effective participation, as well as equal opportunities for leadership, at all levels of decision-making in political, economic, and public life.
Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Supporting the funding of Gold Standard certified Averted Disability Adjusted Life Years (ADALYs) enables organizations to uphold their commitments to promoting good health. By financing projects that lead to certified ADALYs through the Gold Standard, organizations can contribute directly to these health-related goals and targets.
Note: ADALYs are not required to be quantified for SDG 3. A project without ADALYs can also claim a positive contribution to SDG 3. GS4GG impact quantification methodology for ADALYS is an option.
Typical project types which claim this SDG are biogas, improved cook stoves, water filters, etc.
What is eligible for claiming?
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
- SDG Target 3.9: Substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses caused by hazardous chemicals, as well as air, water, and soil pollution and contamination.
- SDG Target 3.9.1: Decrease the mortality rate attributed to household and ambient air pollution.
HOW ARE SDGS SELECTED?
There are 4 main points to selecting the Sustainable Development Goals for a Project:


SDGS PER PROJECT TYPES
An SDG Impact Tool is provided by the Gold Standard Foundation to help in the calculation of these impacts.
GS SDG IMPACT TOOL
Starting from March 13, 2022, the SDG Impact Tool has been released for public utilization and is now a mandatory element in the project development cycle. This tool, presented in an Excel format, provides a standardized template that simplifies the transparent monitoring of SDG impact and carbon reduction efforts. By streamlining the process and reducing associated costs with Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV), the tool facilitates consistent and valuable contributions to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Its implementation guarantees clarity and consistency in tracking SDG impact, while simultaneously promoting cost-effectiveness in the MRV process.

To download the GS SGD Impact tool, click on the button below.





